·
Computer's capabilities and
limitations,
·
How to use computers in different
fields,
·
How the software is developed, and
·
The effects of computer on society
and education.
r
(b) Accuracy: Computers are very accurate. A computer has a tiny chip inside it which does not wear out. The chips have integrated circuits on which electrons (electric pulses) flow. The instructions is wrong the result will bw ambiguous. Such an ambiguity is termed as GIGO (Garbage-In-Garbage-Out). Therefore, the data and instruction must be accurate and specific to the computer.
rrr
(c) Storage: Computers can store huge number of data. Data (sing: datum) are the relevant information given to the computer for processing. The date of birthe, name, class, section are some examples of data. The computers use Hard Disks which have big storage capacity. the tape drive and microfiche are other examples of storage devices wgich have huge data storage capacity.
(d) Diligence: computers do not get tired when a task is performed repeatedly. It is a human-made machine and it does repeated tasks. In the quality control and process control, repeated tasks are performed by the computers.
(e) Versatility: Computers perform data processing at a great speed. The data may be of any kind. It performs processing and gives the result of that processing to a suitable device. A computer perform data processing, spreadsheet calculations and word processing. Thus, computers are versatile in processing tasks.
(f) Reliability: Computers are very much reliable. The components inside the microprocessors do not wear out. The electric pulses move at the rate of speed of light inside the integration does not malfunction.
Computers have Limitations
The limitations of computer can be summarized
as follows:
· Computers
do not have their own thinking capacity.
· Computers
always need stored program for their functionality.
· Computers
need electrical power to operate.
· An
operator is necessary to give instructions to the computer.
1.5 Appearance of Computer
There are numerous manufacturers that produce different of computer. But the computers are mainly manufactured in two principles: Apple/Macintosh and IBM (International BUsiness Machines).Apple/Macintosh computers are mostly used in wordprocessing and spreadsheet calculations. These computers are different from IBM computers in architectural designs.
IBM computers are based on a different principle and architectural design. IBM computers are manufactured by IBM Corporation, USA. The computers which are in use mostly are IBM computers. Compatible means that the principles exist together. IBM compatible computers can perform all the tasks that an IBM computer does. IBM compatible computers are mostly used in data processing, programming, quality control, process control, education, games, word processin, accountancy, etc. You will study the features of IBM compatible computers in this book. Every computer has disk drives. The disks are used as storage device. There may be a hard disk in a personal computer. The two external drives of the computer are : Drive A: and Drive B:. The hard disk is fixed inside the computer. Every computer needs two depending upon individual computer configuration. All computers are not same in processing and speed capabilities. Some computers are very fast and some are slow in processing. A computer has a main chip or processor, commonly called microprocessor. The microprocessor has a serial number. The computers can be classsified on the basis of processors. Some microprocessors are listed below:
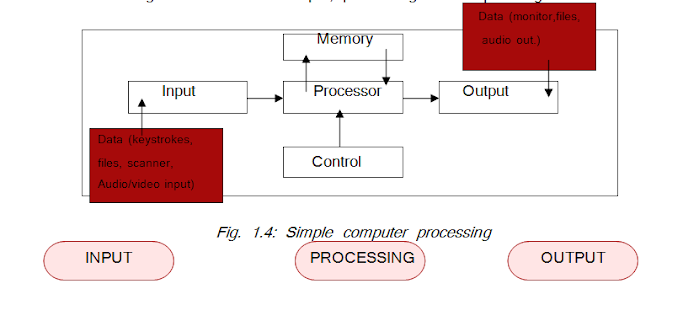
In a computer system, the data is fed through a suitable device. the device may be input device or storage media. THe data is processed by the processor and result of this processing will be displayed on the monitor or on a suitable output device such as printer or plotter. But sometimes, data given to the computer is wrong and the processing output will also be indesirable. Such a phenomenon is called Garbage-In-Garbage-Out (GIGO). The processing operation is performed by the processor inside the computer which is located on the motherboard. The general architect of input, processing and output is given below.
Processing: The computer uses its main processor and supporting processor for analyzing and processing data and instructions.
Output: The computer generates the result of processing which is commonly known as output. The output of the processing is diplayed on the screen, printed or sent to the speaker.
Storage: The computer can store the data, instructions, intermediate results and final results of output on the stprage devices such as hard disk, RAM or optical discs.
The computer's main processor has different sections to perform different tasks. These sections are:
1. Arithmetuc and Logic Unit (ALU),
2. Control Unit(CU), and
3. Memory Unit.
1. Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU): the ALU performs the arithmetic operations and logical operations. The arithmetic operations involve the calculation of numbers such as addition, subtraction, multiplication or division whereas logical operations are comparison between the two data or conditions with the help of suitable operators such as greater than (>), smaller than (<), equal to (=), greater or equal to (>=). The arithmetic and logic section plays storage to arithmetic and logic section or vice-versa.
2. Control Unit (CU): The entire system of the computer gets the instructions, direction, selection, interpretation, execution of program, etc. This section does not process the data but the data and instructions are interpreted in the CU and the other components get the instructions from the Control Section.
3. Memory Unit: Memory Unit holds the data. The data is meant to be processed. This section has the responsibility of holding the data and instruction from the keyboard and Conrol section of the system. The intermediate results are also being held in this section.
Memory is the name for any part of computer that is made to store data. Early computers had vaccum tubes as the memory devices. The vaccum tubes were discovered by Lee De Forest in 1908. The advancement over vaccum tubes were the transistors which were discovered by a team led by William Shockley in 1948. The other members of the team were John Burden and Walter H. Brattain. A transistors functioned equal to 1000 vaccum tubes. Later on, transistors were replaced by integrated circuits. Intergrated circuits were developed by Jack Kilby and Robert Noyace in 1959. But its official authentication for marketing was given to Harwick Johnson of RCA in 1953. Integrated Circuits were called chips. The developments on the chips or integrated circuits are: LSI (Large Scale Integration) and VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration).
Memory of computer is either volatile or non-volatile. The volatile memory is often called RAM (Random Access Memory). The other type of memory is permanent and is called ROM (Read Only Memory). That means RAM is erasable and ROM is not erasable.
(i) Read Only Memory (ROM): ROM (Read Only Memory) is the permanent memory. This type of memory chip stores programs permanently. The program stored in the ROM is called firmware. The recent advancement over ROM are: PROM (Programmable Read Only Memory). EPROM (Erasable and Programmable Read Only Memory), EEPROM (Electrically Erasable and Programmable Read Only Memory).
(ii) Random Access Memory (RAM): Random Access Memory (RAM) is a volatile memory. This is the memory part in which your program, DOS and software you have used fit. The RAM size of each computer may differ. You can increase the size of RAM above 640K which is called extended memory. 640K memory of the computer is base memory. When you switch on the computer, it reads the RAM space in the first place.Random Access Memory can be divided into twomajor categories - the Static RAM (SRAM) and the DynamicRAM (DRAM). Static RAM has the power of storing data aslong as electrical power is given. As soon as the power is putoff, the data and instruction on the SRAM will be washedaway, which cannot be retrieved at all. The Dynamic RAMholds data for a few milisecond and needs periodic refreshing.The refresing usually performed from the main processor of thesystem.Latest computers use new memory system. DDR1,DDR2 and DDR3 are the latest development of Dynamic RAMand they are extensively used in Pentium III and Pentium IVcomputers.1.8 Parts of a Computer SystemThe basic requirement to install a complete computer system are:1. Volt Guard2. Central Processing Unit3. Monitor4. Keyboard5. Printer
1. Volt Guard: Volt guard is the device used to supply poer to the computer. It lies between the computer and the main power supply point of a room. For a personalcomputer, voltage regulator, autocut, voltage stabilizer or UPS (Uninterrupted Power Supply) are the most common. Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS) supplies the power to the computer automatically when electrical power is cut off. This prevents the loss off data.
Printers of microcomputers may have 9 pins, 18 pins or 24 pins. Generally a printer with higher number of pins give better quality of printed output. There are some laser printers in connection with the mainframe computers and minicomputers which can print 64000 lines per minute !
 |
| Printer |
Data: The term data refers to fact or figure. They can be daily expenditure, information about game, numerical calculation, a document, etc.
Information: Information is the processed output. Sometimes, the information thus produced can be data for another processing procedure. The is meaningful to the user and computer. The marks obtained by a student, the division that you get in the examination are information.
Program: A program is set of instruction to the computer. The computer understands its own language. The computer's language is in binary digits. The programs are written using different programming languages such as C, C++ but they are finally converted in the binary format. The programs are designed for instructions.
Hardware: The physical part of the computer known as hardware. The hardware includes electronic components, connectivity wires, circuit on the motherboard or other devices, monitor, mouse, keyboard, etc.
Software: The software is another important component of computer. Computer cannot work without software. Every hardware is controlled by the software. Software is made for specific purpose.
MAIN
POINTS TO REMEMBER
Main Points To Remember:
1. Computers are used in every fiels. Some of the areas where computers are
very successful are:
business, banking, air-traffic,
computer-based, education and training.
2. Computer study is the study of computers, their features, use, limitations
and how the components
are made.
3. Computer literacy means knowing about the use of computers, their features,
limitations, speed,
accuracy, etc.
4. A computer is an electronic device used to manipulate data and instructions
so that it processes
and gives desired result.
5. The capabilities of computers are: speed, accuracy, storage, diligence, versatility
and reliability.
6. Computers do not have their own thinking capacity and they need stored
program to run.
7. IBM and IBM-compatible computers have similar technology whereas Apple/Macintosh
has different
technology.
8. A disk drive is a physical drive which can hols a diskette. The diskette
contains data and program.
The drive reads and writes data and
program onto the disk.
9. A disk contains concentric circles called tracks and different zones called
sectors.
10. The CPU has three sections: ALU, CU and MU.
11. The ALU performs the arithmetic and logical operations.
12. The control unit gives instructions, directions, selection, interpretation
and execution of programs.
13. The memory unit holds the data. There are two types of memory: permanent
menory and
temporary memory.
14. RAM and ROM are examples of Primary memory. Secondary storage device such
as hard disk,
optical disk, floppy disk and
represent secondary memory.
15. RAM is volatle; it loses its content as soon as electricity goes off. ROM
holds the diagnostics of
the computer and instructions called
firmware.
16. The hard disks hold operating system software, programming software and
application software.
17. A computer system is the integration of power supply unit, processing unit,
input unit and output
unit.
18. The monitor is softcopy output unit. The printer is hardcopy output unit.
19. A keyboard is an essential input device for desktop computer.
Full Forms:
BASIC =
Beginner's All purpose Symbolic Instruction Code
GIGO =
Garbage-In-Garbage-Out
ALU
= Arithmetic Logic Unit
CU =
Control Unit
MU =
Memory Unit
LSI =
Large Scale Integration
VLSI =
Very Large Scale Integartion
RAM =
Random Access Memory
SRAM =
Static Random Access Memory
DRAM =
Dynamic Random Access Memory
ROM
= Read Only Memory
PROM = Programmeable
Read Only Memory
EPROM =
Eraseable and Programmeable Read Only Memory
EEPROM =
Electrically Eraseable and Programmeable Read Only Memory
VDU =
Visual Display Unit
CRT =
Cathode Ray Unit
UPS =
Uninterrupted Power Supply
VCR =
Video Cassette Recorder
MDA =
Monochrome Display Adaptor
CGA =
Coloured Graphic Adaptor
MCGA =
Multi-Colored Graphic Adaptor
EGA =
Enhanced Graphic Adaptor
VGA =
Video Graphic Array
SVGA =
Super Video Graphic Array















0 Comments